- Catalog #:1119
- Scientific Name:Plant Sterol Mixture (qualitative)
- Common Name:Plant Sterol Mixture (qualitative)
- SDSView Safety Data Sheet
- Data Sheet:View Data Sheet
- Formula Weight:mixture
- Unit:25 mg/ml, 1ml
- Solvent:chloroform
- Source:natural
- Purity:mixture
- Analytical Methods:TLC, GC
- Natural Source:plant
- Solubility:chloroform
- Physical Appearance:liquid
- Storage:-20°C
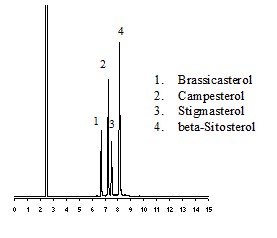
- Composition:Listed in order of elution:
Brassicasterol
Campesterol
Stigmasterol
ß-Sitosterol - Dry Ice:No
- Hazardous:Yes
- Application Notes:
This qualitative mixture contains four major plant sterols isolated from natural sources and is ideal for use as a standard with gas chromatography,1 mass spectrometry, and high performance liquid chromatography. Plant sterols are important components of membranes and have a particular role in the plasma membrane, mitochondrial outer membrane, and endoplasmic reticulum. Plant sterols will complex with glycosphingolipids in raft-like sub-domains and can affect many cellular functions including membrane fluidity, permeability, activity of membrane-bound enzymes, cellular differentiation, cellular signaling, and cellular proliferation. They can be esterified, glycoslilated, and acylated to form steryl esters, steryl glycosides, and acylated steryl glycosides. Sterol esters are usually found only in small amounts naturally but sterol glycosides account for most of the common plant sterols. Plant sterols have been used extensively in humans to attempt to lower cholesterol and treat certain cancers.2 A small amount of plant sterols are consumed by animals and a dysfunction of metabolism can result in sitosterolemia, a high plasma plant sterol concentration.3 This is a qualitative mixture and should not be used for quantitative purposes.
References:
1. L. Clement et al. “Quantitation of Sterols and Steryl Esters in Fortified Foods and Beverages by GC/FID” JAOCS, 2010 electronic publication
2. A. de Jong, J. Plat, R. Mensink “Metabolic effects of plant sterols and stanols (Review)” Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, Vol. 14:7 pp. 362-369, 2003
3. J. Kruit et al. “Plant Sterols Cause Macrothrombocytopenia in a Mouse Model of Sitosterolemia” Journal of Bilogical Chemistry, Vol. 283 pp. 6281-6287